Here are some real-life project examples where the concepts and ideas from this module are put into practice. Are you ready to dive into the case studies?
Visit Empordanet
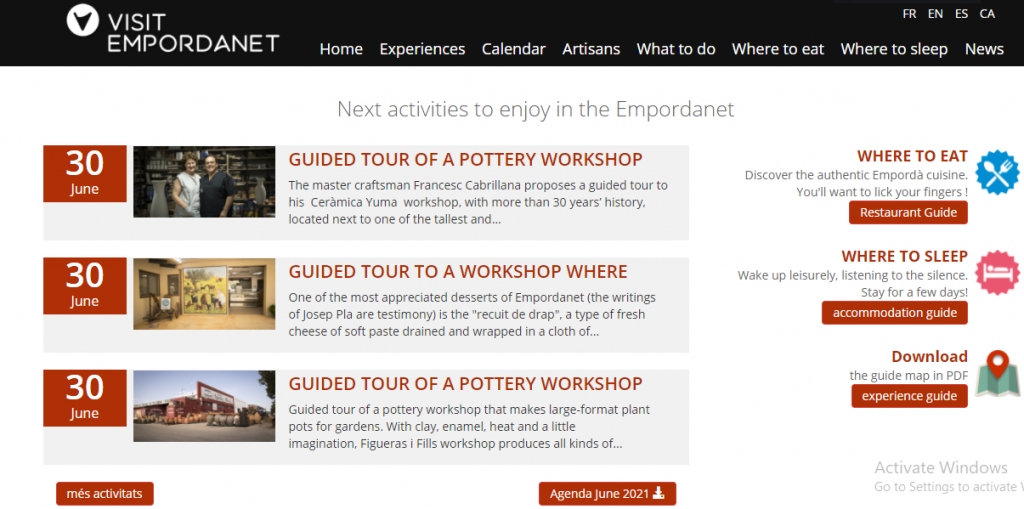
A powerful example of cultural innovation that integrates sustainability, community involvement, and heritage preservation is the creative tourism platform in Spain visitempordanet.com. This initiative highlights how tourism can be built around the intangible cultural heritage of local communities—such as traditional crafts and deep-rooted knowledge of nature. The website acts as a digital catalog, presenting the unique story of the region and offering detailed descriptions of local experiences, hosted by community members themselves. It includes a calendar of guided tours and hands-on workshops, promoting active participation in cultural traditions. By emphasizing storytelling, the platform celebrates the authenticity and uniqueness of each activity, while encouraging visitors to taste, discover, and purchase local products. It is a strong example of strategic tourism planning that not only supports the local economy but also fosters a sense of pride and continuity within the community.
Āraiši Leģendas. Interactive game

Using interactive game apps for digital storytelling offers a dynamic and engaging way to promote cultural heritage and support creative tourism. These apps combine storytelling with game mechanics—such as quests, puzzles, and exploration—to immerse users in local traditions, histories, and landscapes.
An excellent example of digital storytelling through interactive game apps can be found in Āraiši, Latvia. There, the interactive game “Āraišu Leģendas” (“Legends of Āraiši”) was developed as a tourism product using the game application Actionbound. The app, available for free download, guided players through a map featuring culturally significant sites, each linked to local legends. At each stop, users encountered stories, visual content, and questions that deepened their understanding of the area’s heritage. This interactive format not only educated visitors in an entertaining way but also encouraged exploration of the region, making tourism more engaging and accessible through modern technology, especially appreciated among younger travellers.

